Task Parallelism
https://www.coursera.org/learn/parallel-programming-in-java/
Task Creation and Termination (Async, Finish)
以数组求和作为例子
为了求得数组的和,可以将数组分为前后两个部分。两部分的求和可以并行执行,但是在求总和之前要保证两个子任务已经完成。
1 | finish { |
async <stmt1> :父任务创建子任务执行<stmt1>,并且是并行于父任务的其余部分执行
上面的伪代码中,async SUM1;创建子任务SUM1,和SUM2并行执行
finish <stmt2>:父任务执行<stmt2>,并且等待<stmt2>以及其中创建的异步任务完成
上例中,父任务等待SUM1和SUM2完成,才能执行SUM
Tasks in Java’s Fork/Join Framework
数组求和的分治写法
1 | private static class ASum{ |
并行写法
1 | import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool; |
Computation Graphs, Work, Span
Computation Graphs
Computation Graphs (CGs) model the execution of a parallel program as a partially ordered set.
A CG consist of:
- A set of vertices or nodes, in which each node represents a step consisting of an arbitrary sequential computation.
- A set of directed edges that represent ordering constraints among steps.
对于fork-join框架,可以将这些有向边分为三类:
- Continue edges,连接任务中顺序执行的步骤
- Fork edges,将fork操作连接到子任务的第一个步骤
- join edges connect the last step of a task to all join operations on that task
一个小例子
1 | S1 |
对应的CG为
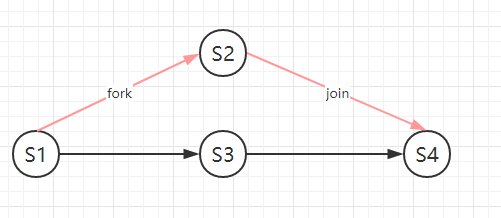
CGs上的data race
没有边连接的两个节点同时写或者读写相同的位置时发生data race
CGs上的理想并行程度 (ideal parallelism)
与计算机的实际并行性无关
$$
ideal,parallelism = \frac{WORK(G)}{SPAN(G)} \tag{1}
$$
其中:
- WORK(G)为G中所有节点执行时间之和
- SPAN(G)为G中关键路径上节点的执行时间之和,上例中SPAN(G)为 max((S1,S3,S4), (S1,S2,S4))
Multiprocessor Scheduling, Parallel Speedup
假设
有P个处理器,每个处理器都相同,每一个节点的执行时间都是固定的(不管在那个处理器上),处理器都是贪心地执行任务
T_p表示在p个处理器上执行一个CG所花的时间,
相同的P个处理器,相同的CG,不同的调度算法也可能对应不同的T_p
$$
T_{\infty} \le T_p \le T_1
$$
Speedup(P)
the parallel speedup for a given schedule of a CG on P processors,满足下面:
$$
Speedup(P) = \frac{T_1}{T_P} \tag{2}
$$
$$
Speedup(P) \le P \tag{3}
$$
$$
Speedup(P) \le \frac {WORK}{SPAN} \tag{4}
$$
(3)表示P个处理器不能带来P倍的加速
(4)表示现实骨感,理想丰满
Amdahl’s Law
if q ≤ 1 is the fraction of WORK in a parallel program that must be executed sequentially, then the best speedup that can be obtained for that program for any number of processors, P , is Speedup(P) ≤ 1*/q*.
例如,如果线性工作占比为0.5,则不管处理器个数再多,有Speedup(P) ≤ 2
因为有
$$
WORK(G)*q \leq SPAN(G) \tag{5}\
==> \frac{WORK(G)}{SPAN(G)} \leq \frac{1}{q}
$$
上式表示关键路径用时不小于任务中线性部分的用时