记录开发 duozhuavue💚 时对 Apollo Client 缓存的处理方法。
为什么要处理缓存?
修改数据后,如果不对缓存中的数据进行修改,那么会造成服务器端和客户端的数据不一致,修改也不能在前端得到体现。
在 duozhuavue💚 中,需要处理缓存的地方有书籍评论,用户书架,主页信息流分页。
缓存处理方法
Apollo Client 提供了几种方式与缓存数据交互
结合开发过程中的具体情况,处理缓存数据时可以采取不同的方式。
书籍评论
后端定义
后端代码中 Book 的 schema 定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| type Book {
id: ID!
title: String!
...
comments: [Comment!]
}
|
有用的信息是,Book 的 comments 字段返回该书的评论列表。
和评论相关的几个 mutation 定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| type Mutation{
...
addComment(bookId: ID!, userId: ID!, content: String!, rating: Int, created: DateTime!): addCommentResponse!
deleteComment(bookId: ID!, commentId: ID!): deleteCommentResponse!
updateComment(commentId: ID!, rating: Int!, content: String, updatedAt: DateTime!): updateCommentResponse!
}
type addCommentResponse implements MutationResponse {
code: String!
success: Boolean!
message: String!
book: Book
comment: Comment
}
type deleteCommentResponse implements MutationResponse {
code: String!
success: Boolean!
message: String!
book: Book
}
type updateCommentResponse implements MutationResponse {
code: String!
success: Boolean!
message: String!
comment: Comment
}
|
从代码可以知道:
addComment 的返回值中包含新生成的 Comment 对象和更新后的 Book 对象deleteComment 的返回值中包含更新后的 Book 对象updateComment 的返回值中包含更新后的 Comment 对象
发送 Mutation
客户端利用 vue-apollo 发送 Mutation 请求。
对缓存的操作主要包括两个部分:
Comment 对象Book 对象的 comments 字段
添加评论
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| export const ADD_COMMENT_MUTATION = gql`
mutation addComment(
$bookId: ID!
$userId: ID!
$content: String!
$created: DateTime!
$rating: Int
) {
addComment(
bookId: $bookId
userId: $userId
content: $content
created: $created
rating: $rating
) {
code
success
message
comment {
id
content
commenter {
name
}
}
book {
id
comments {
content
createdAt
}
}
}
}
`;
const {
mutate: addComment,
loading: addCommentLoading,
onDone,
} = useMutation(ADD_COMMENT_MUTATION, () => ({
variables: {
bookId,
userId,
content: content.value,
created: new Date().toISOString(),
rating: rating.value,
},
}));
onDone(({ data: { addComment } }) => {
router.replace("/books/" + bookId + "?target=book-comment-wrapper");
rating.value = 0;
content.value = "";
});
|
这里没有定义缓存处理方法。原因是:
- 新生成的
Comment 对象,会自动保存在缓存中
- 对于
Book 来说,由于返回了一个相同 id 的 Book 数据,该数据会自动覆盖缓存中的旧数据(Book 中的各个字段都会被覆盖
默认情况下,在缓存中使用对象的类型名+”:”+id 唯一标识一个缓存对象
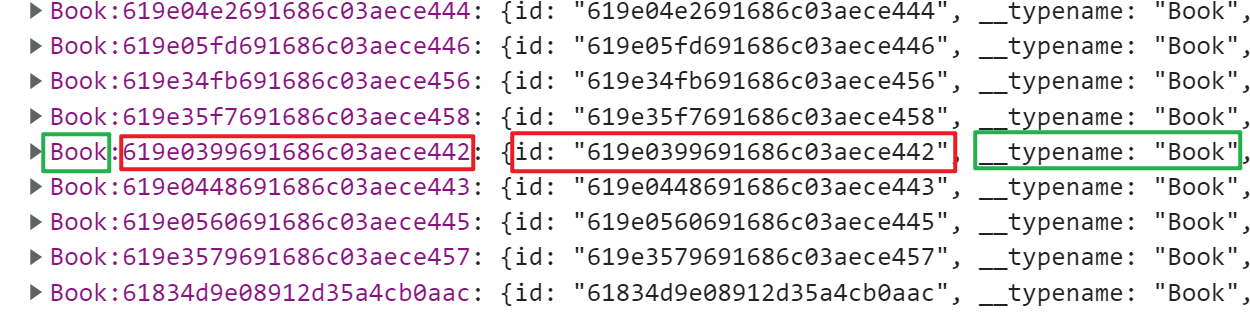
删除评论
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| export const DELETE_COMMENT_MUTATION = gql`
mutation deleteComment($bookId: ID!, $commentId: ID!) {
deleteComment(bookId: $bookId, commentId: $commentId) {
code
success
message
book {
id
comments {
id
content
createdAt
}
}
}
}
`;
const { mutate: deleteComment, onDone: onCommentDelete } = useMutation(
DELETE_COMMENT_MUTATION,
() => ({
variables: {
bookId,
commentId,
},
update: (cache) => {
const normalizedId = cache.identify({
id: commentId,
__typename: "Comment",
});
cache.evict({ id: normalizedId });
cache.gc();
},
})
);
onCommentDelete(({ data: { deleteComment } }) => {
toast.success(deleteComment.message);
router.go(-1);
});
|
这里定义了缓存处理方法
对于 Book.comments 缓存,返回的新数据会自动覆盖旧数据。
👁 当你这样处理时,控制台会发出警告,提示
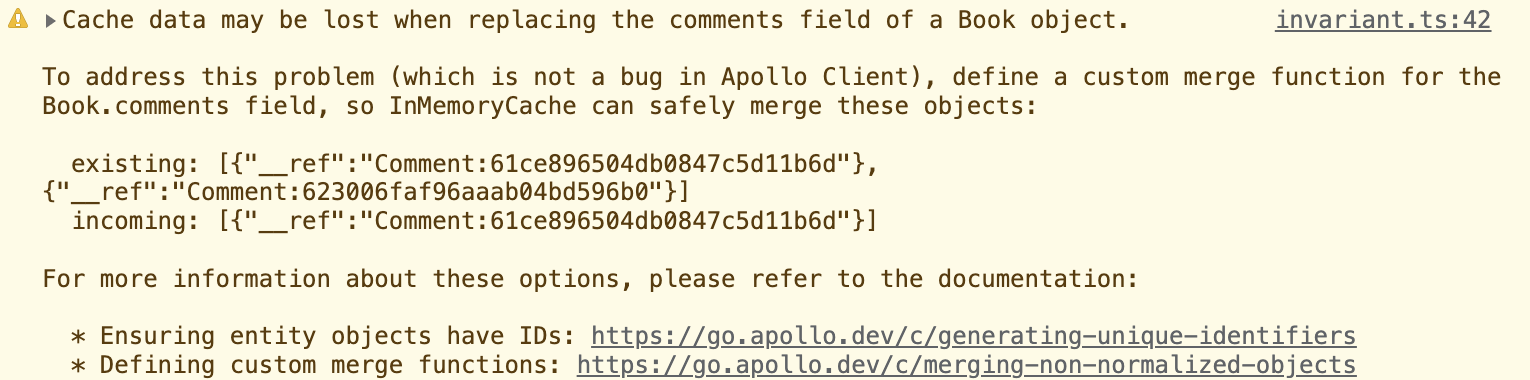
关于控制台警告这里描述了类似的问题,因为默认行为符合需求,所以不需要额外的字段策略设置,可以忽略该警告。
更新评论
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| export const UPDATE_COMMENT_MUTATION = gql`
mutation UpdateComment(
$commentId: ID!
$rating: Int!
$updatedAt: DateTime!
$content: String
) {
updateComment(
commentId: $commentId
rating: $rating
updatedAt: $updatedAt
content: $content
) {
code
success
message
comment {
id
rating
content
createdAt
updatedAt
}
}
}
`;
const {
mutate: updateComment,
loading: isUpdating,
onDone: onCommentUpdate,
} = useMutation(UPDATE_COMMENT_MUTATION, () => ({
variables: {
commentId,
rating: rating.value,
content: content.value,
updatedAt: new Date().toISOString(),
},
}));
onCommentUpdate(({ data: { updateComment } }) => {
if (updateComment.success) {
content.value = "";
rating.value = 0;
toast.success(updateComment.message);
router.go(-1);
} else {
toast.warning(updateComment.message);
}
});
|
这里也没有定义缓存处理方法,原因是:
- 更新
id 为 c1 的评论成功后,会返回 c1 对应的新数据,该数据会自动覆盖旧数据
- 对于
Book 缓存来说,由于 comments 字段中保存的是都是数据引用,因此不需要额外的操作
更新书架
后端定义
User 的 schema 定义如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| type User {
id: ID!
name: String!
...
bookShelf: [Book!]
...
}
|
Query 中定义了一个查询,判断书籍是否在书架中:
1
2
3
4
| type Query {
...
isBookInBookshelf(bookId: ID!, userId: ID!): Boolean!
}
|
书架 Mutation 定义如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| type Mutation {
...
toggleBookshelf(userId: ID!, bookId: ID!): toggleBookshelfResponse!
}
type toggleBookshelfResponse implements MutationResponse {
code: String!
success: Boolean!
message: String!
user: User
}
|
从定义可知:
- 更新书架后,会返回一个新的
user 数据
user.bookShelf 中保存用户书架列表
发送 Mutation
需要处理的缓存内容有:
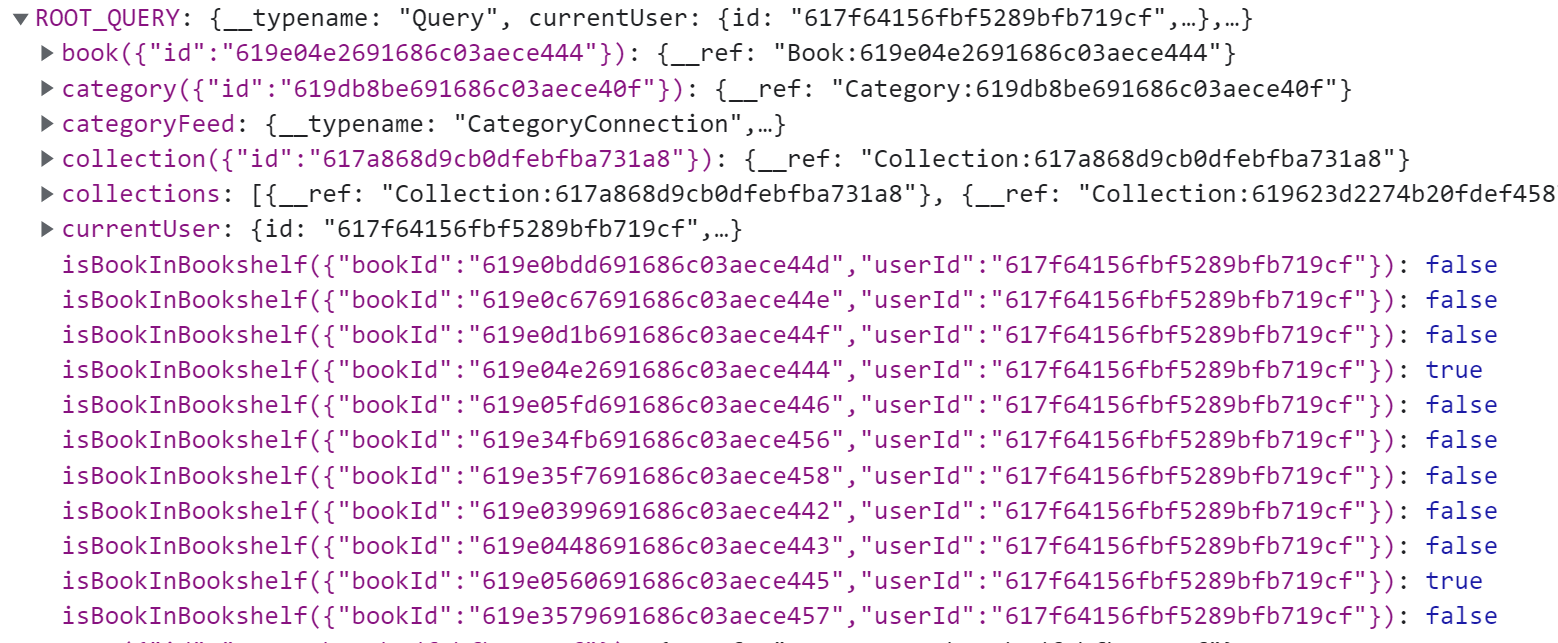
isBookInBookshelf 查询的缓存结果User 的 bookShelf 字段
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| export const GET_IS_BOOK_IN_BOOKSHELF = gql`
query isBookInBookshelf($bookId: ID!, $userId: ID!) {
isBookInBookshelf(bookId: $bookId, userId: $userId)
}
`;
export const TOGGLE_BOOKSHELF_MUTATION = gql`
mutation toggleBookshelf($bookId: ID!, $userId: ID!) {
toggleBookshelf(bookId: $bookId, userId: $userId) {
message
success
user {
id
bookShelf {
title
id
rawAuthor
publisher
publishDate
doubanRating
summary
image
isbn13
}
}
}
}
`;
const { mutate: toggleBookshelf, onDone: onToggle } = useMutation(
TOGGLE_BOOKSHELF_MUTATION,
() => ({
variables: {
bookId: bookId.value,
userId,
},
update: (cache, { data: { toggleBookshelf } }) => {
const oldData = cache.readQuery({
query: GET_IS_BOOK_IN_BOOKSHELF,
variables: {
bookId: bookId.value,
userId,
},
});
if (toggleBookshelf.success === true) {
cache.writeQuery({
query: GET_IS_BOOK_IN_BOOKSHELF,
variables: {
bookId: bookId.value,
userId,
},
data: {
isBookInBookshelf: !oldData.isBookInBookshelf,
},
});
}
},
})
);
|
更新发生后做了两件事:
- 利用
cache.writeQuery 更新 isBookInBookshelf 查询的缓存结果
- 对于
User.bookShelf 字段,由于新的 user 数据会覆盖缓存中的旧数据,因此可以不做处理
💥当前实现的问题
- 每一本书都需要发送一个额外的查询,判断其是否已经在书架中
- 从未登录状态切换到登录状态时,所有已经加载的书籍都会发送
isBookInBookshelf 查询,这意味着用户登录伴随着 N 个额外请求(不可接受!
 重写duozhuavue书架
重写duozhuavue书架
主页信息流分页
开发分页功能时,也进行了一些缓存合并。策略定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| Query: {
fields: {
categoryFeed: relayStylePagination()
}
},
Category: {
fields: {
items: relayStylePagination()
}
},
|
这里利用了 Apollo Client 提供的 relayStylePagination() 工具函数,它已经实现了缓存合并策略。
总结
- 对于缓存中的查询,可以利用
cache.readQuery 和 cache.writeQuery 进行更新
- 对于缓存中的对象,一般情况下返回的新数据会自动覆盖旧数据,也可以利用
cache.modify 修改
- 为了让返回的新对象自动替代缓存中的对象,必须在客户端的
schema 定义中返回 id 字段
- 对于分页信息的缓存,尽可能在设置字段策略时使用
Apollo Client 提供的工具函数,如 offsetLimitPagination(), relayStylePagination()
- 删除缓存中的对象时,先利用
cache.identify 确定缓存对应的标识符,然后使用 cache.evict 和 cache.gc
useMutation 处理缓存的逻辑写在 update 函数中



 重写duozhuavue书架
重写duozhuavue书架